VCSA Low Disk Space Problem - Part 1
It's a very common problem, observing some of the vCenter server's disks are full and also no space remaining causes service interruption, because of possible reasons like massive log or dump files creation. For instance, if you restart the server, some of its services cannot be started, especially VMware PostgreSQL database in the Appliance deployment type. So practically vCenter servers will fail and cannot handle service requests anymore. In the case of VCSA, if you encounter with this issue, maybe you can connect only to the VAMI web page or with the shell access, but there is no vSphere web client UI access, so what should you do in this situation?!
Let's fix it. First of all, shell access is required:
> shell.set --enabled True
> shell
> shell
The result is something like this:
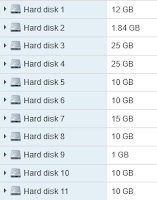
Then we can investigate exist and occupied spaces of VMDKs, so we can choose two methods for saving vCenter: Remove some unnecessary files or Increase the size of vDisks of VCSA.
In some situations like unexpectedly growing log or audit files, saving huge tcpdump exported files in the local storage, many collected netdump files in the ESXi hosts crashing incidents, you will get into this matter, So device what to do highly depends of detecting the root of the problem. I had a critical experience with a failed vCenter that have 0% free space in dev/sda3, and unfortunately, I couldn't enable Bash Shell access, even with: > com.vmware.shell enable.
So you may need to mount the VCSA's VMDKs to another Linux OS (Not as a bootable partition) and clean some of the files to free up disk spaces, then boot the VCSA again to start Bash Shell for its troubleshooting. Selecting an accurate scale of virtual environment in the early steps of VCSA deployment is very important, because wrong selection may lead to saving inventory logs into the disks more than server expectation, so soon enough disk will be filled to cause a problem. In some scenarios after increasing VMDK size by vSphere web client console, then you need to reset the VCSA server for applying Because it will add the not-allocated disk spaces automatically to the old created logical volumes. But if want to do it quickly and cannot restart the server, you can also run following command:
VC_CFG_RESULT=0
It's good to remember that if you deployed an External PSC, in situation of PSC failure (because of low disk space) you should execute this command:
/usr/lib/applmgmt/support/scripts/lvm_cfg.sh storage lvm autogrow
/usr/lib/applmgmt/support/scripts/lvm_cfg.sh storage lvm autogrow




Comments
Post a Comment